[ad_1]

The genes and very important sequences for the regulation of the lac operon are organized such that plenty of mediators can very good tune expression of the three genes inside the operon itself—lacZ, lacYand lacA. The genes lacIwhich encodes the lac repressor, LacIsits exterior the operon and is constitutively expressed. A cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) receptor protein (CRP) binding web site (C) sits in entrance of the promoter space the place there are two potential RNA polymerase binding web sites (P1 andP2). CRP controls the binding of RNA polymerase between P1 andP2 by binding C. Lastly, three operator areas, O1O2and O3are spaced by the DNA space to modulate LacI binding and complete operon repression.
Leaky Repression

When glucose, nonetheless not lactose, is obtainable inside the cell, the LacI binds to the O1 sequence, stopping RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter space. However, ensuing from protein kinetics, a small amount of the lac Gene operon could also be expressed if the polymerase binds when one repressor releases the DNA sooner than one different binds.
Sturdy Activation
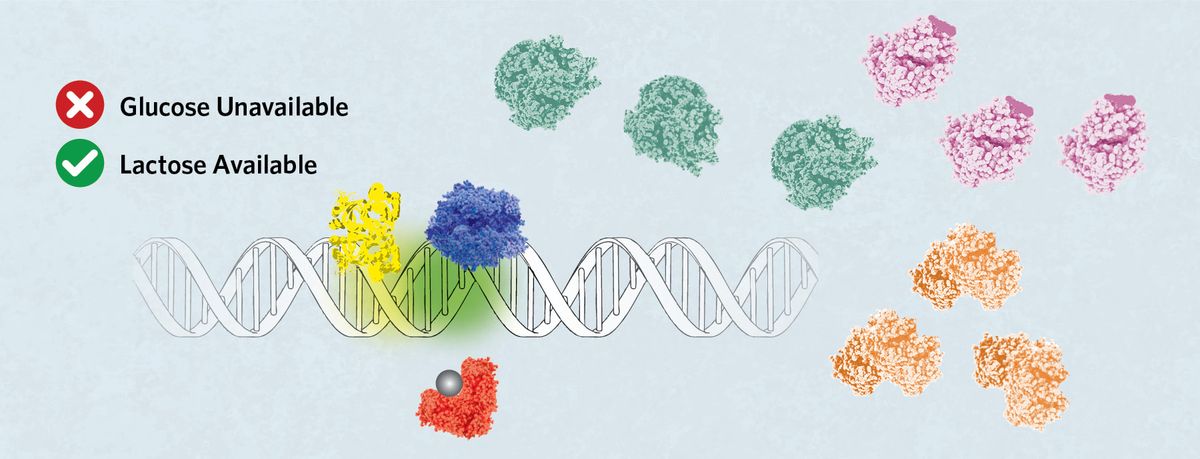
If glucose turns into unavailable nonetheless lactose is present, then allolactose (gray sphere) binds LacI, releasing it from the operator. cAMP, produced inside the absence of glucose, attaches to CRP, prompting its binding to the C web site. This directs the RNA polymerase to sit down down on the P1 web site, which promotes sturdy expression of the lac operon to facilitate lactose digestion.
Tight Repression

The repression of the lac operon inside the absence of lactose could also be improved by DNA looping, whereby LacI binds to O1 and a second operator sequence, each O2 orO3. It will improve the native focus of LacI, decreasing transient expression that occurs when solely free-binding lac repressor is obtainable.1
Weak Activation

When glucose and lactose are every accessible, allolactose releases LacI from the operator, allowing binding of the RNA polymerase. However, inside the absence of cAMP to permit CRP binding, the polymerase binds each P1 orP2 and would not keep on the DNA as efficiently, leading to low expression of the lac gene operon.
Be taught the full story.
[ad_2]
Provide hyperlink
